[codestates] 생성자, 내부 클래스
생성자(Constructor)
생성자는 인스턴스가 생성될 때 호출되는 인스턴스 초기화 메서드입니다.
생성자와 new 를 구별할 필요가 있는데, new 는 인스턴스 생성을 담당, 생성자는 인스턴스 변수들을 초기화하는데 사용하는 메서드입니다.
생성자는 다음과 같은 구조를 가집니다.
- 생성자의 이름은 반드시 클래스의 이름과 같아야 합니다.
- 생성자는 리턴 타입이 없습니다.
class Constructor {
Constructor() { // 생성자 1
System.out.println("1번 생성자");
}
Constructor(String str) { // 생성자 2
System.out.println("2번 생성자");
}
Constructor(int a, int b) { // 생성자 3
System.out.println("3번 생성자");
}
기본 생성자(Default Constructor)
클래스를 만들 때 생성자를 따로 만들지 않았다면 자바 컴파일러가 기본 생성자를 자동으로 추가해줍니다. 만약 이미 추가되어 있는 생성자가 있다면 해당 생성자를 기본으로 사용하게 됩니다.
매개변수가 있는 생성자
매개변수가 있는 생성자는 메서드처럼 매개변수를 받아서 해당값을 인스턴스를 초기화하는 데 사용됩니다. 다음과 같습니다.
class Car {
private String modelName;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed;
public Car(){}
public Car(String modelName, String color, int maxSpeed) {
this.modelName = modelName;
this.color = color;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
}
이렇게 생성자가 여러 개 있는 것을 Contructor Overloading 이라고 합니다.
this vs this()
this()
this() 를 사용해서 같은 클래스 내에서 다른 생성자를 호출할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 규칙을 가집니다.
- this() 는 반드시 생성자의 내부에서만 사용할 수 있습니다.
- this() 는 반드시 생성자의 첫 줄에 위치해야합니다.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Example example = new Example();
Example example2 = new Example(5);
}
}
class Example {
public Example() {
System.out.println("Example의 기본 생성자 호출!");
};
public Example(int x) {
this();
System.out.println("Example의 두 번째 생성자 호출!");
}
}
/*Output
Example의 기본 생성자 호출!
Example의 기본 생성자 호출!
Example의 두 번째 생성자 호출!
*/
this
this 는 참조변수로, 자신이 포함된 인스턴스를 가리킵니다. 일반적인 경우에는 컴파일러가 this. 를 추가해주기 때문에 생략하는 경우가 많습니다.
예를 들어 Car 클래스 내에서 modelName 을 클래스 내부에서 출력하고자 한다면 System.out.println(this.modelName) 처럼 작성해야 하지만, 이 this 는 생략됩니다.
생성자 내에서 this 키워드는 주로 인스턴스의 필드명과 지역변수를 구분하기 위한 용도로 사용됩니다.
class Car {
private String modelName;
private String color;
private int maxSpeed;
public Car(String modelName, String color, int maxSpeed) {
this.modelName = modelName;
this.color = color;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public getModelName(){
System.out.println(modelName); //System.out.println(this.modelName); 와 같다.
}
}
* 생성자 내의 this 는 매개변수와 필드가 구분의 가능할 때 생략가능합니다.
public class StaticTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test("test");
System.out.println(test.name);
}
static class Test {
static String name;
Test(String givenName) {
name = givenName;
}
}
}
Calling Constructors in Superclass
subclass 가 superclass 로부터 생성자를 호출하는 방식입니다. subclass 가 superclass 를 상속받을 때 생성자까지 상속받는 건 아닙니다. 하지만 subclass 는 class 생성자 내에서 superclass 생성자를 무조건 호출해야 합니다.
public class StaticTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car("BMW", "1234");
}
static class Vehicle {
private String regNo = null;
public Vehicle(String no) {
this.regNo = no;
System.out.println("Vehicle constructor2 is called");
}
}
static class Car extends Vehicle {
private String regNo = null;
private String brand = null;
public Car() {}
public Car(String br, String no) {
this.regNo = no;
this.brand = br;
System.out.println("Car constructor is called");
}
}
}
- 위 예제에서 Car 클래스는 Vehicle 클래스를 상속받습니다.
- 이 때 Vehicle 클래스의 기본 생성자는
public Vehicle(String no)입니다. Car 는 현재 super 클래스의 기본 생성자를 호출하고 있지 않기 때문에 다음과 같은 에러가 발생합니다. -
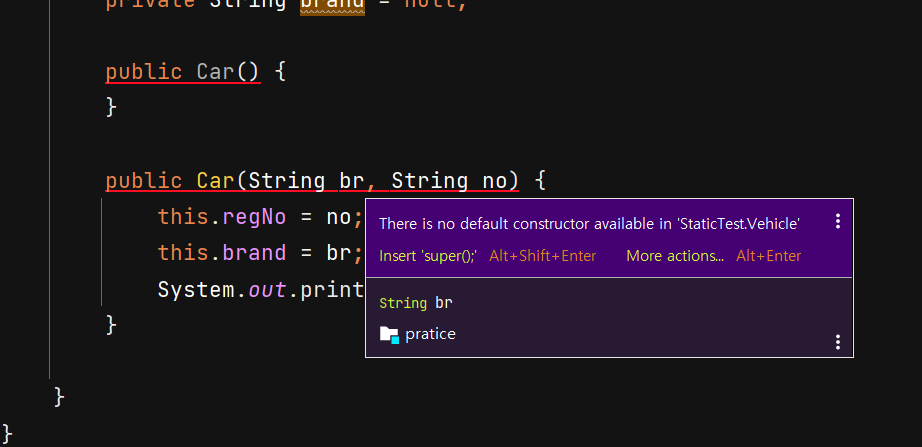
-
따라서 다음과 같이 추가해줄 수 있습니다. regNo 는 부모클래스에서 선언한다고 하겠습니다.
-
static class Vehicle { String regNo = null; public Vehicle(String no) { this.regNo = no; System.out.println("Vehicle constructor2 is called"); } } static class Car extends Vehicle { private String brand = null; public Car() { super("1234"); } public Car(String br, String no) { super(no); this.brand = br; System.out.println("Car constructor is called"); } } - Car 필드 중
regNo를 빼고super(regNo)를 선언하여 superclass 의 생성자를 사용합니다.
-
-
다음과 같이 superclass 의 파라미터가 없는 기본생성자를 추가하여 subclass 에서
super()를 생략해줄 수 있습니다.-
static class Vehicle { //access modifier = protected protected String regNo = null; public Vehicle() { System.out.println("Vehicle constructor1 is called"); } public Vehicle(String no) { this.regNo = no; System.out.println("Vehicle constructor2 is called"); } } static class Car extends Vehicle { private String brand = null; public Car() {} public Car(String br, String no) { this.brand = br; System.out.println("Car constructor is called"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Car car = new Car("BMW", "1234"); System.out.println(car.brand); //BMW System.out.println(car.regNo); //1234, superclass regNo 가 private, default 면 안된다. }
-
- Car 의 인스턴스에서 regNo 를 얻기 위해선 Vehicle 클래스의 regNo 필드의 access modifier 를
protected으로 선언해야 합니다.
Throwing Exceptions From a Constructor
constuctor 에서 예외를 던질 수 있습니다.
public class Car {
public Car(String brand) throws Exception {
if(brand == null) {
throw new Exception("The brand parameter cannot be null!");
}
}
}
throws Exception 은 contructor declaration 의 일부입니다. 따라서 Exception 이 발생하면 created Car instance 은 유효하지 않습니다.
이렇게 예외를 던질 때 다음과 같이 try~catch 로 받을 수 있습니다.
Car car = null;
try{
car = new Car("Mercedes");
//do something with car object
} catch(Exception e) {
// handle exception
}
- constructor 에서 exception 을 던지는 것은 유효하지않은 상태로 만들어지는 인스턴스를 피하기 좋습니다. 유효하지 않은 인스턴스를 만드는 것은 주로 constructor 의 input parameters 이기 때문입니다.
내부 클래스(Inner Class)
inner class 는 클래스 내에 선언된 클래스로, 외부 클래스와 내부 클래스가 서로 연관되어 있을 때 사용합니다. 다음과 같이 이점이 있습니다.
- external class 의 멤버들에 쉽게 접근할 수 있고, 코드의 복잡성을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 외부적으로 불필요한 데이터를 감출 수 있어 캡슐화(encapsulation)를 달성하는 데 유용합니다.
종류는 다음과 같습니다.
| 종 류 | 선언 위치 | 사용 가능한 변수 |
|---|---|---|
| 인스턴스 내부 클래스(instance inner class) | 외부 클래스의 멤버변수 선언위치에 선언(멤버 내부 클래스) | 외부 인스턴스 변수, 외부 전역 변수 |
| 정적 내부 클래스(static inner class) | 외부 클래스의 멤버변수 선언위치에 선언(멤버 내부 클래스) | 외부 전역 변수 |
| 지역 내부 클래스(local inner class) | 외부 클래스의 메서드나 초기화블록 안에 선언 | 외부 인스턴스 변수, 외부 전역 변수 |
| 익명 내부 클래스(anonymous inner class) | 클래스의 선언과 객체의 생성을 동시에 하는 일회용 익명 클래스 | 외부 인스턴스 변수, 외부 전역 변수 |
멤버 내부 클래스
instance inner class 와 static inner class 를 묶어서 member inner class 라고 통칭합니다.
instance inner class
class Outer { //외부 클래스
private int num = 1; //외부 클래스 인스턴스 변수
private static int sNum = 2; // 외부 클래스 정적 변수
private InClass inClass; // 내부 클래스 선언
public Outer() {
inClass = new InClass(); //외부 클래스 생성자
}
class InClass { //인스턴스 내부 클래스
int inNum = 10; //내부 클래스의 인스턴스 변수
void Test() {
System.out.println("Outer num = " + num + "(외부 클래스의 인스턴스 변수)");
System.out.println("Outer sNum = " + sNum + "(외부 클래스의 정적 변수)");
}
}
public void testClass() {
inClass.Test();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
System.out.println("외부 클래스 사용하여 내부 클래스 기능 호출");
outer.testClass(); // 내부 클래스 기능 호출
}
}
// 출력값
외부 클래스 사용하여 내부 클래스 기능 호출
Outer num = 1(외부 클래스의 인스턴스 변수)
Outer sNum = 2(외부 클래스의 정적 변수)
- 다음과 같이 instance inner class 에서는 external class 의 Instance variable 과 static variable 모두를 호출할 수 있습니다.
static inner class
class Outer { // 외부 클래스
private int num = 3; // 외부 클래스의 인스턴스 변수
private static int sNum = 4;
void getPrint() {
System.out.println("인스턴스 메서드");
}
static void getPrintStatic() {
System.out.println("스태틱 메서드");
}
static class StaticInClass { // 정적 내부 클래스
void test() {
System.out.println("Outer sNum = " +sNum + "(외부 클래스의 정적 변수)");
getPrintStatic();
// num 과 getPrint() 는 정적 멤버가 아니라 사용 불가.
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer.StaticInClass a = new Outer.StaticInClass(); //정적 이너 클래스의 객체 생성
a.test();
}
}
//출력값
Outer sNum = 4(외부 클래스의 정적 변수)
스태틱 메서드
- StaticInClass 안에서는 instance 필드, 메서드를 사용하지 못합니다.
지역 내부 클래스
local inner class 는 local variable 과 유사하게 메서드 내부에서만 사용가능합니다. 따라서 일반적으로 메서드 안에서 선언 후 바로 객체를 생성해서 사용합니다. 다음과 같습니다.
class Outer { //외부 클래스
int num = 5;
void test() {
int num2 = 6;
class LocalInClass { //지역 내부 클래스
void getPrint() {
System.out.println(num); //5
System.out.println(num2); //6
}
}
LocalInClass localInClass = new LocalInClass();
localInClass.getPrint();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.test();
}
}
//출력값
5
6



댓글남기기